By: Kendall L. Kerew, Associate Clinical Professor of Law and Director of Externships, Georgia State University College of Law; Holloran Center Fellow
Last month, I had the privilege of participating in the 2023 Wake Forest Law Review Symposium: Leading Change in the Legal Profession.[1] I was part of a panel with Luke Bierman (Elon School of Law) and Maria Savasta-Kennedy (University of North Carolina School of Law) entitled, “Experiential Education and Lawyer Development.” Specifically, the panel “explore[d] the history of experiential education in law schools; the current status of experiential education in American legal education; and the role of experiential education, including clinics, externships, simulations, and more in shaping the professional identity of law students and lawyers.”[2]
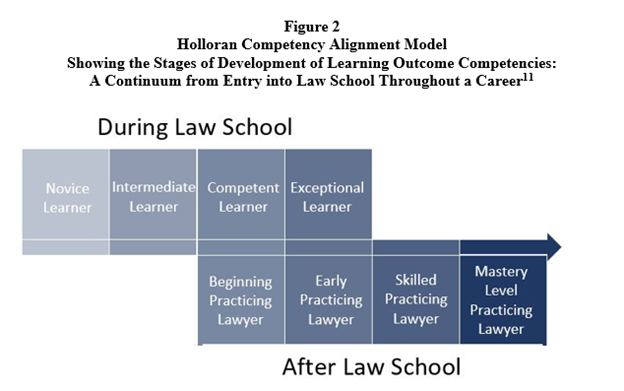
Given the focus of the panel, my prepared remarks enumerated four reasons why experiential education should be central to how we teach law students now and in the future: 1) the requirement that law schools incorporate professional identity formation throughout the curriculum because learning while in the role of lawyer, where a student experiences the integration of knowledge, skills, and values, is particularly well-suited to examining one’s emerging professional identity;[3] 2) the requirement that law schools provide education on bias, cross-cultural competency, and racism because, for students in law clinics or field placements, one of the instances must occur before, concurrently with, or part of students’ enrollment in clinical or field placement courses;[4] 3) the development of the NextGen Bar Exam and efforts to ensure alternative pathways to licensure because the path forward is focused much less on rote memorization and more on the application of knowledge and skills;[5] and 4) the greater role artificial intelligence is likely to play in law practice because experiential education teaches lawyering skills that are uniquely human.
In this blog post, I want to focus on the last reason I posited for why experiential education is particularly relevant to the future of legal education: the greater role artificial intelligence is likely to play in law school and law practice. I am sure you have heard the news stories about ChatGPT writing passing answers to the bar exam and law school exams,[6] how ChatGPT can improve student legal writing,[7] how a judge used ChatGPT to write a ruling,[8] and that ChatGPT may end up making lawyers obsolete.[9] Given all the attention ChatGPT has been getting, I thought it would be interesting to ask ChatGPT the following question and share it as part of my remarks:
What aspects of lawyering cannot be replaced by AI?
This was ChatGPT’s response:
There are several aspects of lawyering that cannot be replaced by AI, including:
Empathy and Emotional Intelligence: Lawyers need to understand their clients’ emotions and needs to provide effective legal advice. AI lacks the ability to comprehend and express emotions, making it difficult for it to replace the empathy and emotional intelligence needed in the legal profession.
Creativity and Critical Thinking: Lawyers often need to come up with creative solutions to complex legal problems. AI, while capable of analyzing vast amounts of data and generating insights, lacks the creativity and critical thinking skills needed to approach legal issues in novel and effective ways.
Advocacy and Persuasion: A significant part of a lawyer’s role involves advocating for their clients’ interests in court or in negotiations. This requires excellent communication skills, the ability to read and respond to non-verbal cues, and the art of persuasion. While AI can analyze and predict the outcome of legal disputes, it cannot advocate for a client in a courtroom.
Ethics and Professionalism: Lawyers are bound by strict ethical and professional standards, which require them to act in the best interests of their clients while upholding the rule of law. AI lacks the moral compass and judgment necessary to make ethical decisions, making it unsuitable for replacing the role of a lawyer.
Client Relationship Management: A lawyer’s success often depends on their ability to build and maintain strong relationships with their clients. AI lacks the ability to build rapport or provide personalized attention to clients, making it difficult to replace the human touch needed in client relationship management.
If you are reading this blog, you probably already knew this and felt secure in the future of our profession. Nonetheless, ChatGPT’s answer encompasses the very things we teach in experiential education and explore through professional identity formation. So for this blog post, I decided to ask ChatGPT a follow-up question:
Why is professional identity formation important to legal education?
This was ChatGPT’s response:
Professional identity formation is essential to legal education because it shapes how law students understand themselves as future lawyers and how they approach their legal careers. A strong professional identity helps students to develop a sense of purpose and a commitment to the values and ethics of the legal profession.
Here are some key reasons why professional identity formation is important to legal education:
Ethical and Professional Conduct: A strong professional identity helps students develop a sense of responsibility towards ethical and professional conduct, which is essential for the effective functioning of the legal system.
Career Satisfaction: By developing a strong professional identity, law students can better understand their strengths and interests, and align them with the legal career path that is most fulfilling to them.
Client Relationships: A strong professional identity can help students develop the skills and mindset needed to build strong relationships with clients based on trust, integrity, and empathy.
Effective Advocacy: Professional identity formation can help law students develop the skills and values needed to be effective advocates for their clients, while still maintaining their own sense of professional ethics.
Overall, professional identity formation is an essential component of legal education, as it helps students develop the knowledge, skills, and values needed to become competent and ethical lawyers.
This response, coupled with ChatGPT’s response to my initial question, reinforced what we already know: professional identity formation is uniquely human and a necessary component of preparing law students to become the lawyers of the future – lawyers who cannot be replaced by artificial intelligence.
Please feel free to reach out to me at kkerew@gsu.edu if you have any questions or comments.

[1] http://www.wakeforestlawreview.com/2023-symposium/.
[2] Id.
[3] See ABA Standards and Rules of Procedure for Approval of Law Schools 2022–2023, Standard 303(b)(3), https://www.americanbar.org/content/dam/aba/administrative/legal_education_and_admissions_to_the_bar/standards/2022-2023/2022-2023-standards-and-rules-of-procedure.pdf; Timothy W. Floyd & Kendall L. Kerew, Marking the Path from Law Student to Lawyer: Using Field Placement Courses to Facilitate the Deliberate Exploration of Professional Identity and Purpose, 68 Mercer L. Rev. 767, 790 (2017).
[4] See ABA Standards and Rules of Procedure for Approval of Law Schools 2022–2023, Standard 303(c), https://www.americanbar.org/content/dam/aba/administrative/legal_education_and_admissions_to_the_bar/standards/2022-2023/2022-2023-standards-and-rules-of-procedure.pdf.
[5] See About the NextGen Bar Exam, https://nextgenbarexam.ncbex.org/ (”Set to debut in July 2026, the NextGen Bar Exam will test on a broad range of foundational lawyering skills, utilizing a focused set of clearly identified fundamental legal concepts and principles needed in today’s practice of law.”).
[6] See Debra Cassesns Weiss, Latest version of ChatGPT aces bar exam with score nearing 90th Percentile, ABA Journal (March 16, 2023), https://www.abajournal.com/web/article/latest-version-of-chatgpt-aces-the-bar-exam-with-score-in-90th-percentile?utm_medium=email&utm_source=salesforce_642881&sc_sid=01075549&utm_campaign=weekly_email&promo=&utm_content=&additional4=&additional5=&sfmc_j=642881&sfmc_s=45062043&sfmc_l=1527&sfmc_jb=18001&sfmc_mid=100027443&sfmc_u=19035492.
[7] See Stephanie Francis Ward, Can ChatGPT help law students to write better? ABA Journal (March 6, 2023), https://www.abajournal.com/web/article/can-chatgpt-help-law-students-learn-to-write-better.
[8] See Columbian judge uses ChatGPT in ruling on child’s medical rights case, CBS News (Feb. 2, 2023), https://www.cbsnews.com/news/colombian-judge-uses-chatgpt-in-ruling-on-childs-medical-rights-case/.
[9] See Jenna Greene, Will ChatGPT make lawyers obsolete (Hint: be afraid), Reuters (Dec. 9, 2022), https://www.reuters.com/legal/transactional/will-chatgpt-make-lawyers-obsolete-hint-be-afraid-2022-12-09/.